题目 | Climbing the Tree
CodeTON Round 4 (Div. 1 + Div. 2, Rated, Prizes!)
D. Climbing the Tree
https://codeforces.com/contest/1810/problem/D
2 seconds / 256 megabytes
standard input / standard output
Problem
The snails are climbing a tree. The tree height is $h$ meters, and snails start at position $0$.
Each snail has two attributes $a$ and $b$ ($a > b$). Starting from the $1$-st day, one snail climbs the tree like this: during the daylight hours of the day, he climbs up $a$ meters; during the night, the snail rests, and he slides down $b$ meters. If on the $n$-th day, the snail reaches position $h$ for the first time (that is, the top of the tree), he will finish climbing, and we say that the snail spends $n$ days climbing the tree. Note that on the last day of climbing, the snail doesn't necessarily climb up $a$ meters, in case his distance to the top is smaller than $a$.
Unfortunately, you don't know the exact tree height $h$ at first, but you know that $h$ is a positive integer. There are $q$ events of two kinds.
- Event of type $1$: a snail with attributes $a$, $b$ comes and claims that he spent $n$ days climbing the tree. If this message contradicts previously adopted information (i. e. there is no tree for which all previously adopted statements and this one are true), ignore it. Otherwise, adopt it.
- Event of type $2$: a snail with attributes $a$, $b$ comes and asks you how many days he will spend if he climbs the tree. You can only give the answer based on the information you have adopted so far. If you cannot determine the answer precisely, report that.
You need to deal with all the events in order.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains a single integer $t$ ($1 \le t \le 10^4$) — the number of test cases. Then follows their description.
The first line of each test case contains one integer $q$ ($1\le q \le 2\cdot 10^5$) — the number of events.
For the following $q$ lines, the first integer of each line is either $1$ or $2$, denoting the event type.
If the event type is $1$, then three integers $a$, $b$, and $n$ ($1\le a,b,n \le 10^9$, $a>b$) follow.
If the event type is $2$, then two integers $a$ and $b$ ($1\le a,b \le 10^9$, $a>b$) follow.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $q$ over all test cases does not exceed $2\cdot 10^5$.
Output
For each test case, output $q$ integers in one line, one for each event, in order. Specifically,
- for each event of type $1$, if you adopt the message, output $1$; if you ignore it, output $0$;
- for each event of type $2$, output an integer denoting the number of days that the snail will spend. If you cannot determine it, output $-1$.
Example
Input
5
3
1 3 2 5
2 4 1
2 3 2
3
1 6 5 1
2 3 1
2 6 2
3
1 4 2 2
1 2 1 3
2 10 2
9
1 7 3 6
1 2 1 8
2 5 1
1 10 9 7
1 8 1 2
1 10 5 8
1 10 7 7
2 7 4
1 9 4 2
9
1 2 1 6
1 8 5 6
1 4 2 7
2 9 1
1 5 1 4
1 5 2 7
1 7 1 9
1 9 1 4
2 10 8
Output
1 2 5
1 -1 1
1 0 1
1 0 -1 0 0 0 1 8 0
1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
Note
In the first test case, we can determine $h=7$ through the first message, so we know the second snail and the third snail need to spend $2$ and $5$ days respectively to reach the top.
Let's show how the second snail climbs:
- During the daylight hours of the $1$st day: climbs up $4$ meters, now at position $4$.
- During the night of the $1$st day: slides down $1$ meters, now at position $3$.
- During the daylight hours of the $2$nd day: climbs up $4$ meters, now at position $7$ (reaches the top).
In the third test case, the second snail's message contradicts the first snail's, because the second snail says he spent $3$ days, and he can climb at most $1+1+2=4$ meters in the first $3$ days. However, the first snail only needs $1$ day to climb $4$ meters.
题解
整体框架
维护一个对树的高度的预测值区间 $(lb,ub]$,初始区间为 $(1,\infty)$
收到信息(事件 $1$):通过给定的 $a,b,n$,计算出新的树高预测值 $(lb',ub']$,若
- $(lb,ub]\cap(lb',ub']=\varnothing$(即 $ub\leq lb'$ 或 $ub'\leq lb$):新信息与已有信息矛盾,拒绝该信息。
- $(lb,ub]\cap(lb',ub']\neq\varnothing$:新信息与已有信息不矛盾,接受该信息,更新 $lb=\max(lb,lb'),ub=\min(ub,ub')$.
收到询问(事件 $2$):通过给定的 $a,b$,判断爬到 $lb$ 需要的天数 $d_{min}$,爬到 $ub$ 需要的天数 $d_{max}$,若
- $d_{min}=d_{max}$:则能够确定爬上树需要的天数为 $d_{min}$.
- $d_{min}\neq d_{max}$:无法确定爬上树需要的天数具体为多少。
上述框架的思路应该比较清晰,该题难点在于如何使用给定信息计算出对应的数据,过程中也有很多坑点。
预测树高
如何通过给定的 $a,b,n$ 计算树高的预测值,例如以下示例,$a=5,b=3,n=3$:
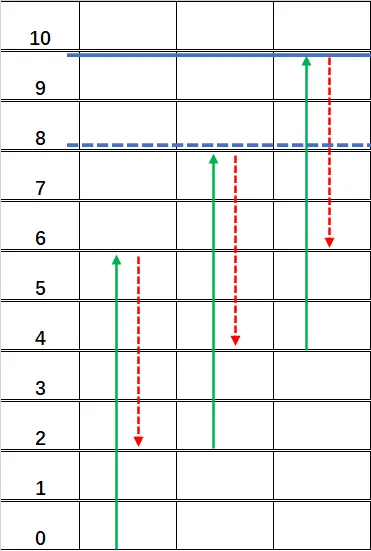
由题意得,$n-1$ 天时爬不上去,$n$ 天时能够爬上去。树高一定大于 $n-1$ 天能够上到的最高点,一定小于等于 $n$ 天能够上到的最高点。所以 $lb$ = $n-1$ 天能够上到的最高点,$ub$ = $n$ 天能够上到的最高点。
我们令 $\Delta h=a-b$,那么可以得到:
- $lb=\Delta h\cdot(n-1)+b$(也可以写做 $\Delta h\cdot(n-2)+a$)
- $ub=\Delta h\cdot(n-1)+a$
易错点:$n=1$ 的情况
若 $n=1$,通过上面的计算会算出来 $lb=b,ub=a$,这是不正确的。因为我们第一次并不是从 $b$ 下滑到 $0$ 后再开始往上爬的,因此 $lb$ 应当是 $0$ 而不是 $b$,如下图所示:
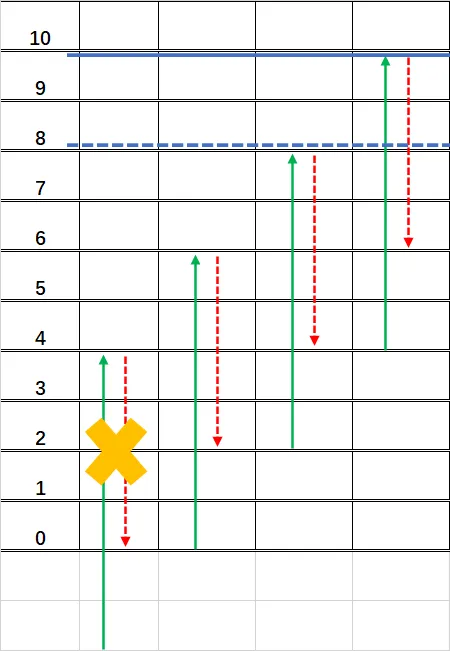
所以 $n=1$ 时,我们需要特判 $lb=0,ub=a$.
预测天数
如何通过给定的 $a,b$ 和树高 $h$ 计算所需天数的预测值,例如以下示例,$a=5,b=3,h=9$:
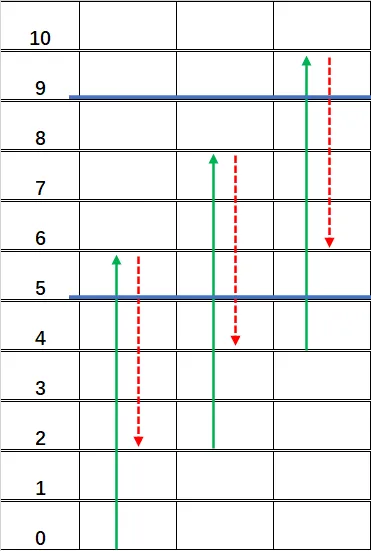
我们知道,最后一天如果爬上树了,就不会再下滑了,这给我们编程带来了一点麻烦。
为了将问题统一化,我们不妨让最后一天也会下滑,那么问题就能看做:每天向上爬 $\Delta h$,几天能够爬到 $h-b$ 高度。
这个问题就很简单了:$d=\lceil(h-b)/\Delta h\rceil$
向上取整的实现方式可以参考以下两种:$\lceil a/b\rceil=(a-1)/b+1=(a+b-1)/b$
易错点:区间是左开右闭的
我们的树高区间为 $(lb,ub]$,是左开右闭的,因此刚好爬到 $lb$ 高度是不算完成的,得爬到 $lb+1$ 高度才算作完成。因此:
- $d_{min}=\lceil(lb+1-b)/\Delta h\rceil$
- $d_{max}=\lceil(ub-b)/\Delta h\rceil$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
void solve()
{
int q;
cin >> q;
int lb = 1, ub = 1e18;
while (q--)
{
int op;
cin >> op;
if (op == 1)
{
int a, b, n;
cin >> a >> b >> n;
int delta = a - b;
int _lb, _ub;
if (n == 1)
{
_lb = 0;
_ub = a;
}
else
{
_lb = delta * (n - 1) + b;
_ub = delta * (n - 1) + a;
}
if (_lb >= ub || _ub <= lb)
{
cout << 0 << ' ';
continue;
}
lb = max(lb, _lb);
ub = min(ub, _ub);
cout << 1 << ' ';
}
else // if (op == 2)
{
int a, b;
cin >> a >> b;
int delta = a - b;
int _min = max(1LL, ((lb + 1) - b + (delta - 1)) / delta);
int _max = max(1LL, (ub - b + (delta - 1)) / delta);
if (_min == _max)
cout << _min << ' ';
else
cout << -1 << ' ';
}
}
cout << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}本文采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可,本文 Markdown 源码:Haotian-BiJi
so Strong