题目 | Keep Connect
UNIQUE VISION Programming Contest 2022(AtCoder Beginner Contest 248)
F - Keep Connect
https://atcoder.jp/contests/abc248/tasks/abc248_f
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MB
Score : $500$ points
Problem Statement
You are given an integer $N$ greater than or equal to $2$ and a prime $P$.
Consider the graph $G$ with $2N$ vertices and $(3N-2)$ edges shown in the figure below.
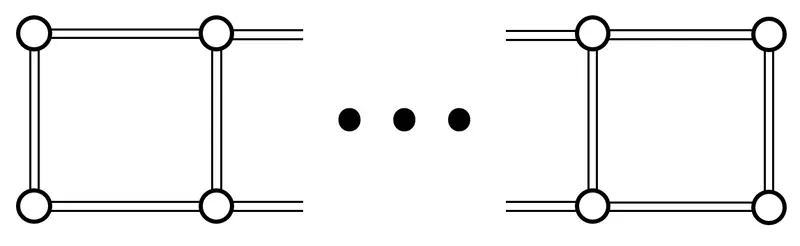
More specifically, the edges connect the vertices as follows, where the vertices are labeled as Vertex $1$, Vertex $2$, $\ldots$, Vertex $2N$, and the edges are labeled as Edge $1$, Edge $2$, $\ldots$, Edge $(3N-2)$.
- For each $1\leq i\leq N-1$, Edge $i$ connects Vertex $i$ and Vertex $i+1$.
- For each $1\leq i\leq N-1$, Edge $(N-1+i)$ connects Vertex $N+i$ and Vertex $N+i+1$.
- For each $1\leq i\leq N$, Edge $(2N-2+i)$ connects Vertex $i$ and Vertex $N+i$.
For each $i=1,2,\ldots ,N-1$, solve the following problem.
Find the number of ways, modulo $P$, to remove exactly $i$ of the $3N-2$ edges of $G$ so that the resulting graph is still connected.
Constraints
- $2 \leq N \leq 3000$
- $9\times 10^8 \leq P \leq 10^9$
- $N$ is an integer.
- $P$ is a prime.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
$N$ $P$
Output
Print $N-1$ integers, the $i$-th of which is the answer for $i=k$, separated by spaces.
Sample Input 1
3 998244353
Sample Output 1
7 15
In the case $N=3$, there are $7$ ways, shown below, to remove exactly one edge so that the resulting graph is still connected.

There are $15$ ways, shown below, to remove exactly two edges so that the resulting graph is still connected.
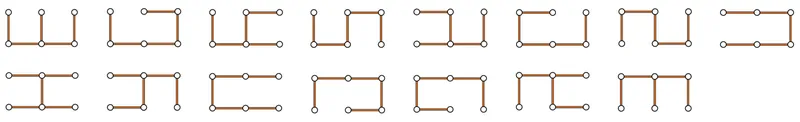
Thus, these numbers modulo $P=998244353$ should be printed: $7$ and $15$, in this order.
Sample Input 2
16 999999937
Sample Output 2
46 1016 14288 143044 1079816 6349672 29622112 110569766 330377828 784245480 453609503 38603306 44981526 314279703 408855776
Be sure to print the numbers modulo $P$.
我的笔记
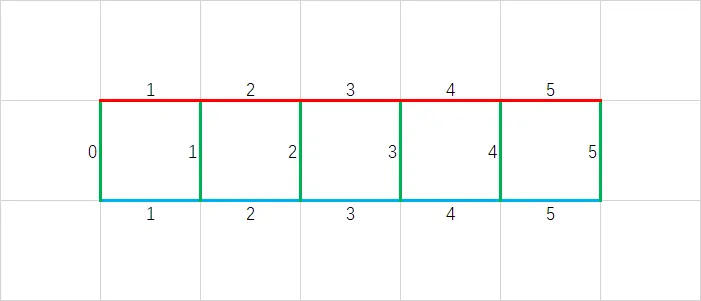
首先将这个图的边 $E$ 分成三种:
- $E_{a_1},E_{a_2},\dots,E_{a_{N-1}}$,即顶部的边,编号 $i=1,2,\dots,N-1$,如下图红边;
- $E_{b_1},E_{b_2},\dots,E_{b_{N-1}}$,即底部的边,编号 $i=1,2,\dots,N-1$,如下图蓝边;
- $E_{c_0},E_{c_1},\dots,E_{c_{N-1}}$,即中间的边,编号 $i=0,1,\dots,N-1$,如下图绿边。
然后把这个图的顶点 $V$ 分成两种:
- $V_{a_0},V_{a_1},\dots,V_{a_{N-1}}$,即上面的一排点;
- $V_{b_0},V_{b_1},\dots,V_{b_{N-1}}$,即下面的一排点。
定义图 $G_i$:包含边 $E_{a_1},E_{a_2},\dots,E_{a_i}$、$E_{b_1},E_{b_2},\dots,E_{b_{i}}$、$E_{c_0},E_{c_1},\dots,E_{c_{i}}$,包含点 $V_{a_0},V_{a_1},\dots,V_{a_i}$、$V_{b_0},V_{b_1},\dots,V_{b_i}$。
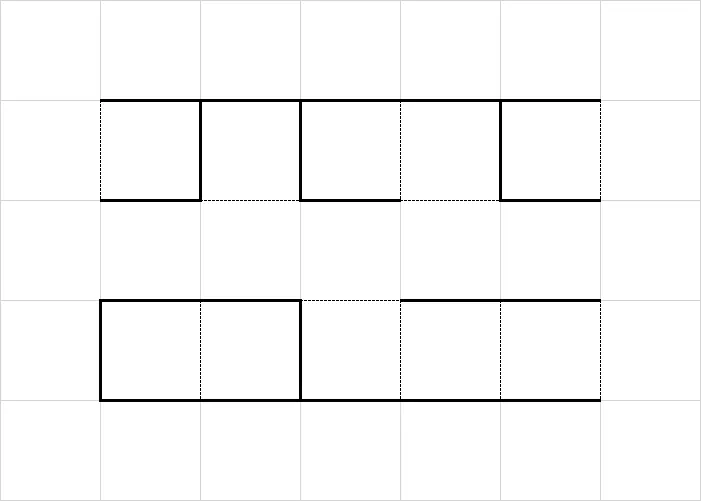
将图 $G_i$ 的状态分成两种:
- 状态 $0$:图联通,如下图中上侧图。
- 状态 $1$:图不连通,但有两个联通子图,并且两子图分别包含 $V_{a_i}$、$V_{b_i}$,如下图中下侧图。
然后运用动态规划思想,$dp[i][j][k]:=$ 在子图 $G_i $中,去除 $j$ 条边后,处于状态 $k$ 的图的数量。
首先初始化 $dp$ 数组,$G_0$ 只有一条边 $E_{c_0}$,要么去要么不去,因此 $dp[0][0][0]=1$,$dp[0][1][1]=1$。
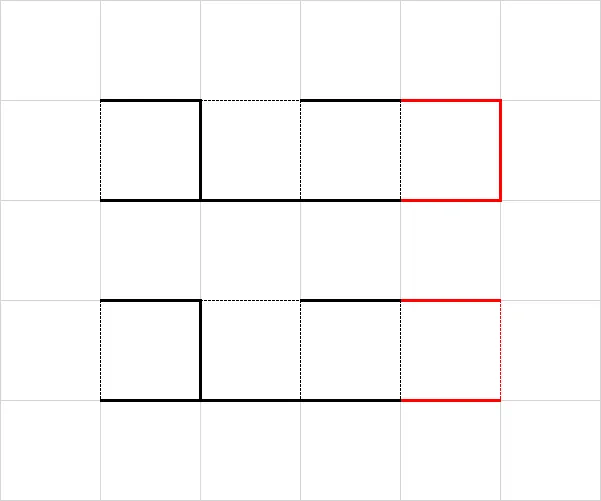
然后寻找递推方法,先思考 $dp[i-1][j][1]$ 的情况:
如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 都保留,那么这个图会变成状态 $0$,如下图上面的情况(红色为新加的边)
- 递推式:$dp[i][j][0]$ += $dp[i-1][j][1]$
如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{c_i}$,那么这个图仍然为状态 $1$,如下图下面的情况
- 递推式:$dp[i][j+1][1]$ += $dp[i-1][j][1]$
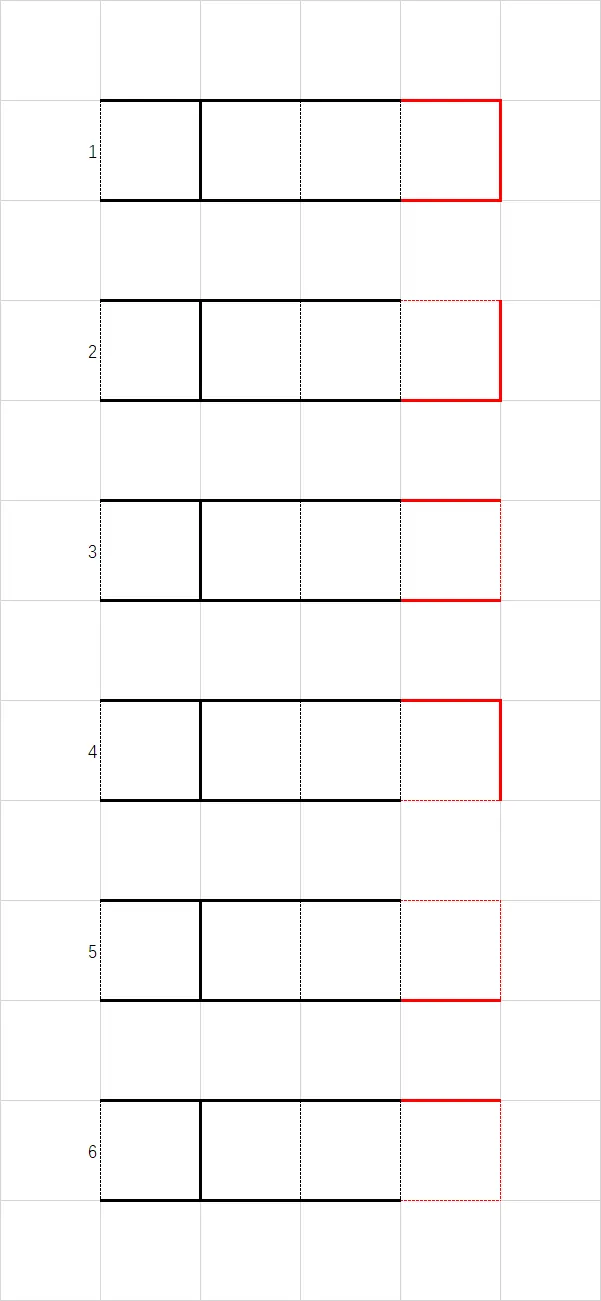
再考虑 $dp[i-1][j][0]$ 的情况:
如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 都保留,那么这个图仍然为状态 $0$,如下图 $1$ 号情况(红色为新加的边)
- 递推式:$dp[i][j][0]$ += $dp[i-1][j][0]$
- 如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{a_i}$,那么这个图仍然为状态 $0$,如下图 $2$ 号情况
- 如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{c_i}$,那么这个图仍然为状态 $0$,如下图 $3$ 号情况
如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{b_i}$,那么这个图仍然为状态 $0$,如下图 $4$ 号情况
- 递推式均为:$dp[i][j+1][0]$ += $dp[i-1][j][0]$
- 如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{a_i},E_{c_i}$,那么这个图会变成状态 $1$,如下图 $5$ 号情况
如果新加的三条边 $E_{a_i},E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$ 去掉 $E_{b_i},E_{c_i}$,那么这个图会变成状态 $1$,如下图 $6$ 号情况
- 递推式均为:$dp[i][j+2][1]$ += $dp[i-1][j][0]$
时间复杂度:$O(N^2)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 3100;
long long dp[MAXN][MAXN][2];
int N, P;
int main()
{
dp[0][0][0] = 1;
dp[0][1][1] = 1;
cin >> N >> P;
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
{
dp[i][j][0] += dp[i - 1][j][1];
dp[i][j][0] %= P;
dp[i][j + 1][1] += dp[i - 1][j][1];
dp[i][j + 1][1] %= P;
dp[i][j][0] += dp[i - 1][j][0];
dp[i][j][0] %= P;
dp[i][j + 1][0] += 3 * dp[i - 1][j][0];
dp[i][j + 1][0] %= P;
dp[i][j + 2][1] += 2 * dp[i - 1][j][0];
dp[i][j + 2][1] %= P;
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
cout << dp[N - 1][i][0] << ' ';
return 0;
}本文采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可,本文 Markdown 源码:Haotian-BiJi