题目 | Least Prefix Sum
Hello 2023
C. Least Prefix Sum
https://codeforces.com/contest/1779/problem/C
2 seconds / 256 megabytes
standard input / standard output
Problem
Baltic, a famous chess player who is also a mathematician, has an array $a_1,a_2, \ldots, a_n$, and he can perform the following operation several (possibly $0$) times:
- Choose some index $i$ ($1 \leq i \leq n$);
- multiply $a_i$ with $-1$, that is, set $a_i := -a_i$.
Baltic's favorite number is $m$, and he wants $a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_m$ to be the smallest of all non-empty prefix sums. More formally, for each $k = 1,2,\ldots, n$ it should hold that
$$ a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_k \geq a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_m. $$
Please note that multiple smallest prefix sums may exist and that it is only required that $a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_m$ is one of them.
Help Baltic find the minimum number of operations required to make $a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_m$ the least of all prefix sums. It can be shown that a valid sequence of operations always exists.
Input
Each test contains multiple test cases. The first line contains the number of test cases $t$ ($1 \leq t \leq 10\,000$). The description of the test cases follows.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $n$ and $m$ ($1 \leq m \leq n \leq 2\cdot 10^5$) — the size of Baltic's array and his favorite number.
The second line contains $n$ integers $a_1,a_2, \ldots, a_n$ ($-10^9 \leq a_i \leq 10^9$) — the array.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ over all test cases does not exceed $2\cdot 10^5$.
Output
For each test case, print a single integer — the minimum number of required operations.
Example
Input
6
4 3
-1 -2 -3 -4
4 3
1 2 3 4
1 1
1
5 5
-2 3 -5 1 -20
5 2
-2 3 -5 -5 -20
10 4
345875723 -48 384678321 -375635768 -35867853 -35863586 -358683842 -81725678 38576 -357865873
Output
1
1
0
0
3
4
Note
In the first example, we perform the operation $a_4 := -a_4$. The array becomes $[-1,-2,-3,4]$ and the prefix sums, $[a_1, \ a_1+a_2, \ a_1+a_2+a_3, \ a_1+a_2+a_3+a_4]$, are equal to $[-1,-3,-6,-2]$. Thus $a_1 + a_2 + a_3=-6$ is the smallest of all prefix sums.
In the second example, we perform the operation $a_3 := -a_3$. The array becomes $[1,2,-3,4]$ with prefix sums equal to $[1,3,0,4]$.
In the third and fourth examples, $a_1 + a_2 + \cdots + a_m$ is already the smallest of the prefix sums — no operation needs to be performed.
In the fifth example, a valid sequence of operations is:
- $a_3 := -a_3$,
- $a_2 := -a_2$,
- $a_5 := -a_5$.
The array becomes $[-2,-3,5,-5,20]$ and its prefix sums are $[-2,-5,0,-5,15]$. Note that $a_1+a_2=-5$ and $a_1+a_2+a_3+a_4=-5$ are both the smallest of the prefix sums (and this is a valid solution).
题解
题意
给定一个序列 $a_1,a_2, \ldots, a_n$ 和下标 $m$,通过翻转(乘 $-1$)任意位,让第 $m$ 位的前缀和 $\leq$ 整个序列的所有前缀和。问最少翻转几次。
思路
对下标 $x$ 进行操作,下标 $\geq x$ 的前缀和大小关系不变
下图为前缀和的折线图,我们对 $a_2$ (即 $B$ 点)进行操作,即 $a_2$ 变成 $-a_2$.
可以看到变化是 $\geq2$ 的部分整体向下偏移了 $2a_2$,而该部分内部的大小关系没有变化。
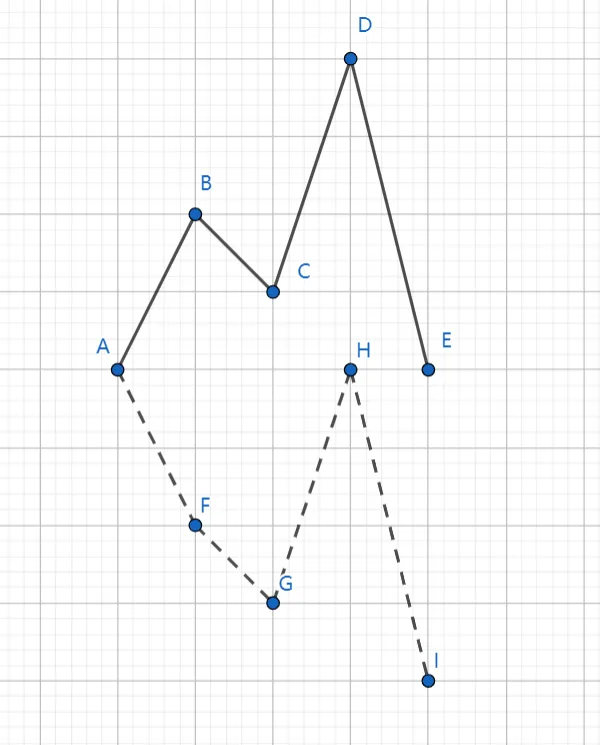
这个结论的作用是,我们对下标 $x$ 进行操作,不会改变 $\geq x$ 部分的合法性。若操作前 $\geq x$ 部分的已经符合条件,操作后也是符合条件的。
对 $>0$ 的元素 $a_i$ 进行操作,能让 该元素及其右侧 偏移 $-2a_i$;
对 $<0$ 的元素 $a_i$ 进行操作,能让 该元素及其右侧 偏移 $+2a_i$.
如下图,我们对 $a_4$(即 $D$ 点)进行操作,可见它及其右侧向下偏移了 $2\times3=6$.
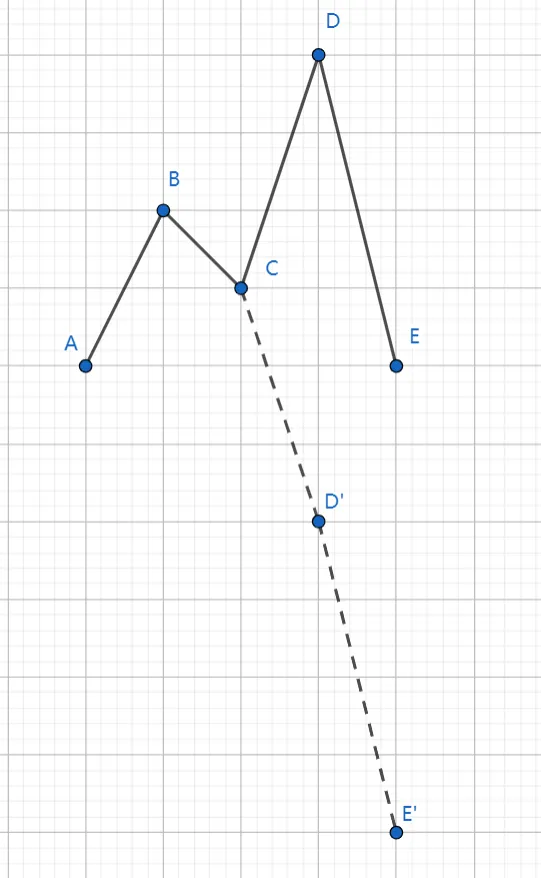
并且,$>0$ 时,若 $a_i$ 越大,向下偏移量就越大;$<0$ 时 $a_i$ 越小,向上偏移量最大。
由于我们要操作次数最小,根据贪心,我们肯定选的是当前的最值进行操作。(这点非常重要,我就是因为比赛时一直没想到这点,一直陷入错误的思维。没做出来这题的人很多都是这点漏掉了)
对于 $m$ 左侧的区间,如果出现不合法,则对最大的元素进行操作
从 $m$ 遍历到 $1$,如果发现第 $x$ 位前缀和不合法(即 $presum_x<presum_m$),则寻找 $(x,m]$ 中最大的元素 $a_i$(一定 $>0$),对其进行操作,操作数 $+1$.
由于 $i<m$,所以操作后 $a_m$ 一定会受到影响而向下偏移 $2a_i$. 我们只需要更新 $presum_m$ 即可,因为其他的前缀和大小关系不变,我们用不上就不需要考虑了。
对于 $m$ 右侧的区间,如果出现不合法,则对最小的元素进行操作
从 $m+1$ 遍历到 $n$,如果发现第 $x$ 位前缀和不合法(即 $presum_x<presum_m$),则寻找 $[m+1,n]$ 中最小的元素 $a_i$(一定 $<0$),对其进行操作,操作数 $+1$.
由于 $i<x$,所以操作后 $a_x$ 及其右侧一定会收到影响而向上偏移 $2a_i$. 我们记录一个 $offset$ 变量,即可得知右侧目前偏移了多少。
最大最小值的维护方法
使用 STL 优先队列即可实现
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int a[MAXN], ps[MAXN];
void solve()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ps[i] = ps[i - 1] + a[i];
int psm = ps[m], cnt = 0, offset = 0;
priority_queue<int> big_heap;
for (int i = m; i >= 1; i--)
{
while (ps[i] < psm + offset)
{
cnt++;
offset -= big_heap.top() * 2;
big_heap.pop();
}
if (a[i] > 0)
big_heap.push(a[i]);
}
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> small_heap;
offset = 0;
for (int i = m + 1; i <= n; i++)
{
if (a[i] < 0)
small_heap.push(a[i]);
while (ps[i] + offset < psm)
{
cnt++;
offset -= small_heap.top() * 2;
small_heap.pop();
}
}
cout << cnt << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}本文采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可,本文 Markdown 源码:Haotian-BiJi