题目 | Counting Graphs
Codeforces Round 891 (Div. 3)
G - Counting Graphs
https://codeforces.com/contest/1857/problem/G
2 seconds / 256 megabytes
standard input / standard output
Problem
Given a tree consisting of $n$ vertices. A tree is a connected undirected graph without cycles. Each edge of the tree has its weight, $w_i$.
Your task is to count the number of different graphs that satisfy all four conditions:
- The graph does not have self-loops and multiple edges.
- The weights on the edges of the graph are integers and do not exceed $S$.
- The graph has exactly one minimum spanning tree.
- The minimum spanning tree of the graph is the given tree.
Two graphs are considered different if their sets of edges are different, taking into account the weights of the edges.
The answer can be large, output it modulo $998244353$.
Input
The first line contains an integer $t$ ($1\le t\le 10^4$) — the number of test cases.
The first line of each test case contains two integers $n$ and $S$ ($2 \le n \le 2 \cdot 10^5, 1\le S\le 10^9$) — the number of vertices and the upper bound of the weights.
Then follow $n-1$ lines describing the tree, the $i$-th line contains three integers $u_i$, $v_i$, and $w_i$ ($1\le u_i,v_i\le n, u_i \ne v_i, 1\le w_i\le S$) — an edge in the tree with weight $w_i$.
It is guaranteed that the sum of $n$ for all tests does not exceed $2\cdot 10^5$.
Output
For each test, output the number of different graphs that satisfy the conditions, modulo $998244353$.
Example
Input
4
2 5
1 2 4
4 5
1 2 2
2 3 4
3 4 3
5 6
1 2 3
1 3 2
3 4 6
3 5 1
10 200
1 2 3
2 3 33
3 4 200
1 5 132
5 6 1
5 7 29
7 8 187
7 9 20
7 10 4
Output
1
8
80
650867886
Note
In the first sample, there is only one graph, which is the given tree.
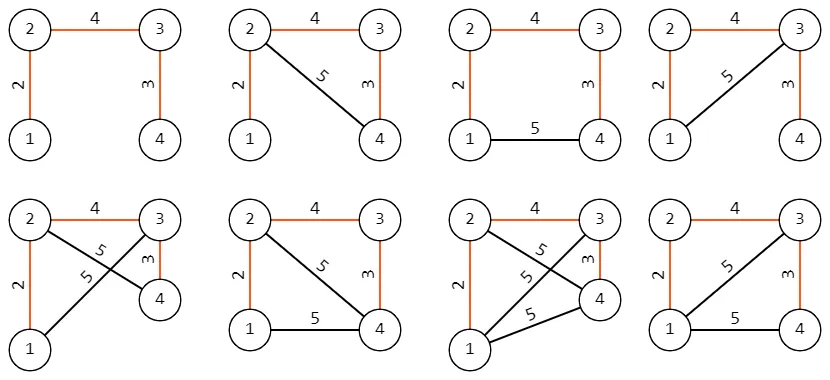
In the second samle, the given tree looks like this:

All possible graphs for the second sample are shown below, the minimum spanning tree is highlighted in red:
题解
考虑 Kruskal 最小生成树算法的过程,在算法过程中每次都是选择的最小不成环的边作为最小生成树的边。本题这个问题就相当于,如何往最小生成树中插入新边,而不干扰最小生成树的形状。
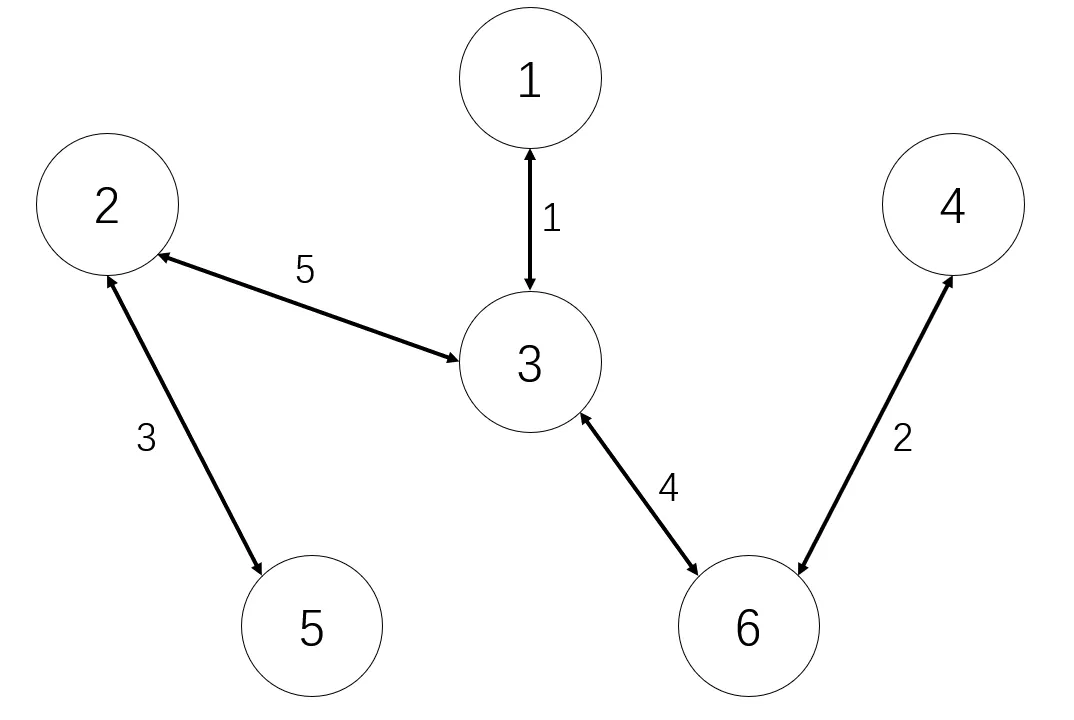
那么容易想到,插入的边比选择的最小边的权重大,那么就可以保证 Kruskal 选边的时候仍然选择原来的那个最小边。例如下面这个最小生成树,在 Kruskal 算法选择权重为 $4$ 的边时,如果插入一条新的 $1\overset{5}\leftrightarrow6$ 边,那么在 Kruskal 的过程中,这条边由于权重比 $4$ 大,所以一定不会被选中,所以不会生成树的形状造成干扰。
那么就直接进行 Kruskal 算法的流程,且额外维护并查集的连通分量大小 $\text{siz}(\cdot)$。在 Kruskal 算法过程插入 $u\overset{w}\leftrightarrow v$ 边的过程中,维护答案:
$$ \text{ans}\leftarrow \text{ans}+(S-w+1)^{\text{siz}(\text{fa}(u))\cdot\text{siz}(\text{fa}(v))-1} $$
公式解释如下:
可选权重范围为 $(w,S]$,共 $S-w$ 种可选。之所以 $+1$ 是因为还可以选择不连这条边(也可以看作权重为 $+\infty$).
$u$ 所在连通分量的元素个数为 $\text{siz}(\text{fa}(u))$,$v$ 所在连通分量的元素个数为 $\text{siz}(\text{fa}(v))$,那么一共可以组合出 $\text{siz}(\text{fa}(u))\cdot\text{siz}(\text{fa}(v))$ 条边。之所以 $-1$ 是因为要排除掉已确定的最小生成树的那条边(因为题目不允许重边).
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define endl '\n'
#define int long long
using namespace std;
constexpr int MOD = 998244353, MAXN = 2e5 + 10;
int fa[MAXN], siz[MAXN];
void init(int n)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
fa[i] = i;
siz[i] = 1;
}
}
int find(int x)
{
return (fa[x] == x) ? x : (fa[x] = find(fa[x]));
}
void merge(int aa, int bb)
{
fa[aa] = bb;
siz[bb] += siz[aa];
}
int quick_pow(int a, int b)
{
int ans = 1;
a %= MOD;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1)
ans = ans * a % MOD;
b >>= 1;
a = a * a % MOD;
}
return ans;
}
void solve()
{
int n, S;
cin >> n >> S;
init(n + 10);
vector<array<int, 3>> edge(n + 10);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
cin >> edge[i][0] >> edge[i][1] >> edge[i][2];
sort(edge.begin() + 1, edge.begin() + n, [](array<int, 3> a, array<int, 3> b)
{ return a[2] < b[2]; });
int ans = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
auto &[u, v, w] = edge[i];
int uu = find(u), vv = find(v);
ans = ans * quick_pow(S - w + 1, siz[uu] * siz[vv] - 1) % MOD;
merge(uu, vv);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
signed main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
solve();
return 0;
}本文采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 许可,本文 Markdown 源码:Haotian-BiJi